Investing in ETFs, or exchange-traded funds, has become an increasingly popular choice for those looking to diversify their portfolios and access various markets.
Understanding how to invest in ETFs requires knowledge of the different types available, alongside the steps necessary for a successful investment.
By harnessing the benefits of ETFs, investors can enjoy lower costs and greater flexibility compared to traditional mutual funds.
Before diving into the specifics, it is essential for investors to recognise that a well-chosen ETF can help achieve long-term financial goals.
This guide will provide a step-by-step approach, making the investment process accessible and straightforward.
Readers will learn about selecting the right ETFs, setting up an investment account, and establishing a strategic investment plan.
This comprehensive guide caters to beginners and experienced investors alike.
With clear instructions and valuable insights, it equips individuals with the tools needed to navigate the ETF landscape confidently.
Understanding how to invest in ETFs could be the key to unlocking potential growth in any investment strategy.
Understanding ETFs and Their Benefits
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) have transformed the investment landscape by offering a blend of flexibility, accessibility, and diversification.
What Is an ETF?
An ETF is a type of investment fund that is traded on stock exchanges, much like individual stocks. It holds a collection of assets, which can include stocks, bonds, and even commodities.
The primary appeal of ETFs lies in their ability to track an index or a specific sector, enabling investors to obtain broad market exposure.
ETFs are composed of various securities, making them an excellent way to diversify a portfolio.
They are structured to be cost-effective, as they typically have lower expense ratios compared to mutual funds.
Additionally, ETFs can be bought and sold throughout the trading day, offering liquidity and flexibility for investors.
Benefits of Investing in ETFs
Investors can enjoy multiple benefits when investing in ETFs. One of the most significant advantages is diversification.
By purchasing a single ETF, investors can gain exposure to a wide range of assets, reducing individual security risk.
ETFs also offer cost benefits. With typically lower management fees and no sales loads, ETFs allow investors to retain a larger portion of their returns.
The trading flexibility is another significant benefit; investors can execute trades any time the market is open, unlike mutual funds, which settle at the end of the trading day.
Additionally, ETFs are generally more tax-efficient than mutual funds, primarily due to their unique structure, which helps minimise capital gains distributions.
ETFs vs Mutual Funds
While both ETFs and mutual funds are pooled investment vehicles, they differ in several key aspects.
ETFs trade on exchanges like individual stocks, allowing for instant buying and selling. In contrast, mutual funds are purchased at the end of the trading day at the net asset value (NAV).
Cost structures also differ. ETFs tend to have lower expense ratios, while mutual funds often charge higher fees for management.
Furthermore, ETFs offer greater transparency because holdings are disclosed daily, whereas mutual funds typically disclose their holdings quarterly.
In terms of investment strategies, diversified portfolios can be created through both funds, but ETFs may provide a more flexible approach, particularly for investors looking to involve strategies such as short selling.
Types of ETFs: Active vs Passive
ETFs can be classified into two main categories: active and passive.
Passive ETFs track a specific index, aiming to replicate its performance. They are designed to offer broad market exposure and typically come with lower management fees.
Active ETFs, on the other hand, are actively managed by portfolio managers who aim to outperform their designated benchmarks.
This approach can potentially lead to higher returns, but it often comes with increased fees and risks associated with active management.
Both types of ETFs provide unique opportunities for investors.
Passive ETFs are ideal for those seeking a simple, low-cost investment, while active ETFs may appeal to those looking for potential higher returns through expert management.
Preparation for ETF Investing
Before diving into ETF investing, it is essential to lay a solid groundwork. This involves evaluating personal risk tolerance and establishing specific financial goals.
Understanding these elements helps in creating a diverse and balanced investment portfolio tailored to individual circumstances.
Assessing Your Risk Tolerance
Evaluating risk tolerance is crucial for any investor. Individual risk levels vary significantly based on factors such as age, financial situation, and investment experience.
An investor can assess their risk tolerance through self-questioning or by using online questionnaires.
Common categories of risk tolerance include:
- Conservative: Prioritises capital preservation; prefers low-risk investments.
- Moderate: Willing to accept some risk for potential growth; balances risk and reward.
- Aggressive: Seeks high returns; comfortable with substantial volatility.
Understanding one’s risk profile aids in selecting ETFs that align with these preferences, ensuring the investment portfolio is not only diversified but also meets the investor’s comfort level during market fluctuations.
Setting Financial Goals
Establishing clear financial goals helps an investor focus their ETF strategy. Goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
This method provides clarity and direction for investment decisions.
Examples of financial goals may include:
- Retirement Savings: Building a nest egg for the future.
- Education Funding: Accumulating funds for children’s college expenses.
- Wealth Accumulation: Growing assets over a predetermined period for major purchases.
When setting goals, consider the time horizon and necessary investment to reach those targets.
Clearly defined goals guide the choice of ETFs, as well as the level of diversification needed in the investment portfolio to mitigate risks effectively.
How to Select the Right ETF
Selecting the appropriate ETF involves analysing various factors that influence performance and cost-effectiveness. Investors should focus on performance metrics, expense ratios, diversification levels, and critical trading information.
Evaluating ETF Performance and Expense Ratio
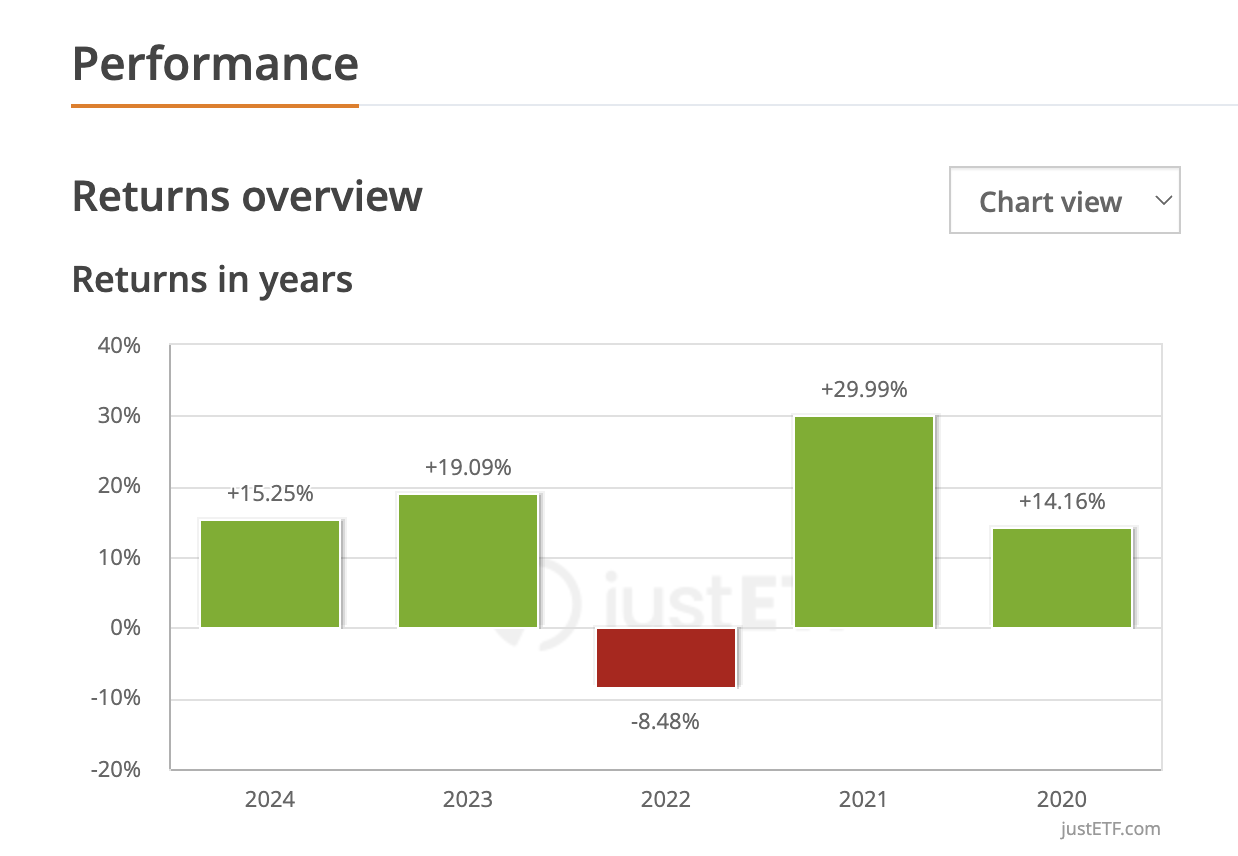
When assessing an ETF’s performance, key indicators include historical returns, tracking error, and volatility.
Historical returns offer insights into how well an ETF replicates its benchmark index, such as the FTSE 100 or other market segments.
The expense ratio is another crucial factor. This ratio reflects the fund’s operating costs, expressed as a percentage of assets.
Lower expense ratios generally enhance net returns for investors. A common threshold for a competitive ETF is an expense ratio below 0.50%.
Analysing Diversification within ETFs
Diversification is essential in mitigating risk. An ETF that tracks a broad index, such as the Nasdaq, typically offers a diverse portfolio.
Investors should evaluate the number of holdings and the sectors represented.
For example, the ARK Innovation ETF provides exposure to various sectors, including technology and genomics.
It’s vital to consider whether the ETF focuses on niche markets or offers a wider range of asset classes. A well-diversified ETF can help balance potential risks against expected returns.
Understanding Ticker Symbols and Trading Information
Ticker symbols identify ETFs on stock exchanges. Each symbol is unique and provides insight into the fund’s focus.
For instance, an investor might see “ARKK” representing the ARK Innovation ETF.
It is also important to understand trading information, such as average daily volume and bid-ask spreads.
High trading volumes generally indicate better liquidity, allowing investors to enter and exit positions more easily.
Assessing these factors aids in making informed decisions when selecting an ETF to invest in.
Setting Up Your Investment Account
Establishing an investment account is a crucial step in the process of investing in ETFs. This involves selecting a suitable brokerage, understanding the differences between online brokers and robo-advisors, and funding the account properly to start trading.
Choosing a Brokerage Account
Choosing the right brokerage account is essential for successful ETF investing.
Investors can select from various types of brokerage accounts, including traditional brokers or online platforms.
It is important to consider factors such as trading fees, account maintenance charges, and the platform’s user interface.
For example, popular options such as eToro and IG offer user-friendly experiences with competitive fees, making them attractive to many investors.
Moreover, some brokers provide educational resources and tools that can significantly benefit beginners.
A comparison of brokerage options will ensure that investors select one that aligns with their investment goals and trading style.
Online Brokers and Robo-Advisors
Online brokers and robo-advisors cater to different investor needs and preferences.
Online brokers typically offer more control, allowing investors to execute trades and manage investments independently.
Investors can execute orders, track performance, and access research tools with platforms like IG that enable customised trading strategies.
On the other hand, robo-advisors, which use algorithms to manage portfolios, are ideal for those who prefer a hands-off approach.
They provide automated investment management tailored to individual goals and risk tolerance.
Robo-advisors often come with lower fees compared to traditional brokers, making them a cost-effective option for many.
Funding Your Account
Once the brokerage account is selected, the next step is to fund it.
Most platforms allow users to deposit funds through various methods, including bank transfers or debit cards.
Investors should review the platform’s deposit options and associated fees to ensure a seamless transaction process.
For instance, eToro allows easy funding through multiple options, which can facilitate quicker access to the markets.
It is also essential for investors to decide how much they want to invest in ETFs.
This can be influenced by factors such as investment goals, risk tolerance, and financial situation.
Proper funding is crucial, as it enables investors to purchase shares and start building their ETF portfolio effectively.
Executing Trades and Building a Portfolio
Understanding how to execute trades effectively and construct a portfolio is crucial for investors.
Key techniques involve choosing the right order type and exploring commission-free trading options, which can enhance investment outcomes.
Additionally, strategies like dollar-cost averaging help mitigate risks associated with market fluctuations.
How to Buy an ETF: Market Orders and Limit Orders
When buying an ETF, investors typically use two main order types: market orders and limit orders.
- Market Orders: This type executes a buy order at the current market price. It’s best used when immediate execution is desired. However, investors should be cautious, as prices can change rapidly.
- Limit Orders: These allow investors to set a specific price at which to buy the ETF. If the market price doesn’t reach this limit, the order remains unfilled. This strategy is beneficial for controlling entry points but may result in missed opportunities if the price doesn’t reach the limit.
Understanding these orders helps in executing trades effectively.
Commission-Free Trading and Investment Options
Many platforms now offer commission-free trading, which can significantly reduce the cost of buying and selling ETFs.
This option enables investors to trade more frequently without worrying about fees that could eat into profits.
Furthermore, various investment options exist within the ETF space.
Investors can choose between equity ETFs, bond ETFs, and sector-specific ETFs to diversify their portfolios.
This flexibility allows for tailored investment strategies, enhancing potential returns while managing risk.
Applying Strategies: Dollar-Cost Averaging
Dollar-cost averaging is a disciplined investment approach where an investor allocates a fixed amount of money to buy ETFs at regular intervals.
This strategy helps smooth out the effects of market volatility.
By consistently investing over time, investors avoid the pitfalls of trying to time the market.
Whether prices are high or low, they purchase shares, potentially lowering the average cost per share over time.
This method aligns well with a passive investing philosophy, encouraging long-term wealth accumulation rather than frequent trading.
Portfolio Management and Growth
Rebalancing and Diversifying Your Portfolio
Rebalancing is essential for maintaining a diversified portfolio.
Investors should periodically review asset allocation to ensure it aligns with their risk tolerance.
For instance, if stocks outperform and rise to make up a larger percentage of the portfolio, selling some of those shares can restore balance.
Diversification reduces risk by spreading investments across different sectors and asset classes.
A well-diversified portfolio may include various ETFs representing equities, bonds, commodities, and international markets.
It is crucial to consider each investment’s correlation to others, aiming for a mix that mitigates risk without sacrificing potential returns.
Tracking Performance and Dividends
Monitoring performance is key to understanding the effectiveness of an investment strategy.
Investors should review total returns, comparing them against benchmarks.
Tools like performance calculators can provide insights into how well an ETF is performing relative to its category or index.
Dividends contribute significantly to total returns and should not be overlooked.
Investors can track dividend yields and payment history to evaluate the income generated by their holdings.
Regularly assessing how dividends are reinvested can enhance long-term growth, as reinvested dividends can leverage the power of compounding.
Advanced Strategies and Considerations
Investing in ETFs can be nuanced, and understanding advanced strategies is essential for maximising potential returns.
Key concepts include asset allocation tailored to individual goals and the specific strategies associated with leveraged and inverse ETFs.
Asset Allocation and Tactical ETF Investing
Asset allocation involves distributing investments among various asset categories, such as equities, fixed income, and commodities.
This strategy helps manage risk while aiming for the desired return.
ETFs enable efficient diversification, allowing investors to own a wider array of assets without significant capital investment.
Tactical ETF investing focuses on short-term market opportunities.
Investors identify trends and make adjustments to their portfolio based on market conditions.
This strategy may involve weighing sectors differently or rotating in and out of particular ETFs based on economic indicators.
For instance, during a market downturn, an investor might shift to defensive ETFs, which can provide better stability.
Leveraged and Inverse ETFs
Leveraged ETFs use financial derivatives to amplify the returns of an underlying index.
For example, a 2x leveraged ETF aims to deliver twice the daily return of its benchmark.
While the potential for higher returns is appealing, the risk of substantial losses increases.
Inverse ETFs, on the other hand, are designed to profit from declines in an index.
They can serve as a hedge against market downturns, allowing investors to maintain a position in falling markets.
Both leveraged and inverse ETFs are typically suitable for experienced investors who actively monitor their portfolios, as they can experience volatility and compounding effects over time.
Conclusion
Investing in ETFs offers a straightforward way to build a diversified portfolio.
Their simplicity makes them accessible for both novice and experienced investors.
With ETFs, individuals can easily invest in a wide range of assets without needing extensive market knowledge.
This approach supports passive investing, allowing for potential long-term growth with lower maintenance.
Key benefits of ETFs include:
- Low Costs: Many brokers offer commission-free trading.
- Diversification: ETFs typically comprise multiple securities, reducing individual stock risk.
- Flexibility: Investors can trade ETFs throughout the trading day like stocks.
The passive nature of ETFs aligns well with modern investment strategies.
Investors benefit from steady growth trends rather than attempting to time the market.
In summary, ETFs combine ease of use with effective investment strategies. They represent a reliable choice for those aiming to invest securely and intelligently.